Introduction
Stumbled upon the term “0 Ohm Resistor” in your electronics journey?
A 0 Ohm Resistor, often referred to as a jumper or wire link, is a special component in the electronics world. It’s a resistor that essentially has no resistance, creating a free path for current. This unique feature makes it an essential tool in PCB and PCBA manufacturing, aiding in circuit flexibility and PCB trace bridging.
In this article, we’ll delve deeper into the realm of 0 Ohm Resistors, unpacking their types, applications, advantages, and design considerations. This guide aims to demystify 0 Ohm Resistors, making them accessible and understandable, no matter your background or level of expertise. Ready to unravel the mystery of 0 Ohm Resistors? Let’s get started!
What is a 0 Ohm Resistor?
In the vast universe of electronics, a 0 Ohm Resistor stands out as a unique component. At first glance, the term might seem contradictory. After all, isn’t the primary function of a resistor to resist or limit the flow of electrical current? So, what does a resistor with zero resistance mean?
A 0 Ohm Resistor, also known as a jumper resistor or a wire link, is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In the case of a 0 Ohm Resistor, the resistance is, as the name suggests, zero ohms. This means that it offers no resistance to the current flowing through it.
In essence, a 0 Ohm Resistor acts like a straight wire, allowing electrical current to pass through freely without any significant voltage drop or impedance. It’s like an open highway for electrons, with no traffic jams or roadblocks to slow them down.
While it might seem odd to have a resistor that doesn’t resist, the 0 Ohm Resistor plays a crucial role in circuit design and PCB manufacturing. Its unique properties make it a versatile tool, enabling circuit flexibility, PCB trace bridging, and a host of other applications that we’ll explore in the following sections.
Types of 0 Ohm Resistors
0 Ohm Resistors come in various types, each suited to different applications. The most common types include:
- Surface Mount (SMT) 0 Ohm Resistors: These are designed to be mounted directly onto the surface of a PCB. They are small, lightweight, and ideal for high-density mounting.
- Through-Hole 0 Ohm Resistors: These are designed to be inserted into holes drilled in the PCB and then soldered into place. They are typically used in applications where higher power ratings are required.
- Chip 0 Ohm Resistors: These are tiny resistors that are used in integrated circuits (ICs) and microchips. They are used to connect different layers within the chip.
Each type of 0 Ohm Resistor has its own advantages and is suited to specific applications, which we’ll explore in more detail in the following sections. So, now that we’ve answered the question, “What is a 0 Ohm Resistor?”, let’s delve deeper into its uses and benefits in the world of electronics.
Applications of 0 Ohm Resistors

0 Ohm Resistors, despite their seemingly simple function, are integral to various applications in the electronics industry. Let’s delve into some of these applications:
Circuit Flexibility and Modifications
0 Ohm Resistors are often used to provide flexibility in circuit design. They allow engineers and designers to make quick and reversible modifications to PCB layouts. By simply placing or removing 0 Ohm Resistors, connections can be easily changed or rerouted as needed during prototyping or troubleshooting.
PCB Trace Bridging
One of the primary uses of 0 Ohm Resistors is to bridge PCB traces, effectively connecting two points on the board. This is crucial for joining different sections of a circuit or creating alternate signal paths, enhancing the overall functionality and performance of the electronic system.
Temporary Component Placement
Throughout the assembly process or testing phase, 0 Ohm Resistors can serve as convenient placeholders for components. This enables effortless addition or removal of other elements at a later stage, all without requiring any alterations to the PCB layout.
Fuse Replacement and Over-current Protection
In certain scenarios, 0 Ohm Resistor can be used as fuse replacements to provide over-current protection. When a fault or excessive current occurs, the 0 Ohm Resistor acts as a sacrificial element, protecting other components from damage. This method offers a more accessible and replaceable solution compared to traditional fuses.
Current Shunt and Sensing
0 Ohm Resistors can be utilized as current shunts for low-current measurement and sensing applications. By measuring the voltage drop across the 0 Ohm Resistor, the current flowing through the circuit can be accurately measured.
Testing and Debugging
During the testing and debugging phase of PCB development, 0-ohm resistors can be temporarily inserted or removed to isolate specific parts of the circuit, facilitating troubleshooting.
These examples illustrate the versatility and utility of 0 Ohm Resistors in electronics. Their unique properties make them an invaluable tool in PCB and PCBA manufacturing, contributing to the efficiency, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness of the process.
Absolutely, let’s proceed with the “Benefits of Using 0 Ohm Resistors” section. Here’s the draft:
Benefits of Using 0 Ohm Resistors
While we’ve explored the various applications of 0 Ohm Resistors, it’s equally important to understand the benefits they bring to these applications. Here are some key advantages of using 0 Ohm Resistors in your electronic designs:
Cost-Effective
One of the primary benefits of 0 Ohm Resistors is their cost-effectiveness. Compared to other components used for similar purposes, 0 Ohm Resistors are generally more affordable. This makes them a go-to choice for designers looking to keep costs down while maintaining high-quality performance.
Versatility
0 Ohm Resistors are incredibly versatile. As we’ve seen, they can be used in a wide range of applications, from bridging PCB traces to acting as placeholders for components. This versatility makes them a valuable addition to any electronic design.
Compatibility with Standard SMT Equipment
Another significant advantage of 0 Ohm Resistors is their compatibility with standard Surface Mount Technology (SMT) equipment. They can be easily placed and soldered by automated pick-and-place machines, which streamlines the manufacturing process and reduces assembly time and costs.
Facilitates Easy Modifications
0 Ohm Resistors allow for easy and reversible modifications to PCB layouts. This is particularly beneficial during the prototyping or troubleshooting stages, where circuit connections may need to be altered or rerouted.
Enhances Signal Integrity
In high-frequency and RF circuits, 0 Ohm Resistors can be used for impedance matching to optimize signal transfer, reduce reflections, and improve signal integrity. This can significantly enhance the performance of critical applications.
Provides Over-Current Protection
In certain scenarios, 0 Ohm Resistors can act as fuse replacements to provide over-current protection. This can protect other components from damage, enhancing the overall reliability and longevity of the device.
These benefits make 0 Ohm Resistors an invaluable tool in PCB and PCBA manufacturing. Their unique properties contribute to the efficiency, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness of the process, making them a popular choice among electronics engineers and designers.
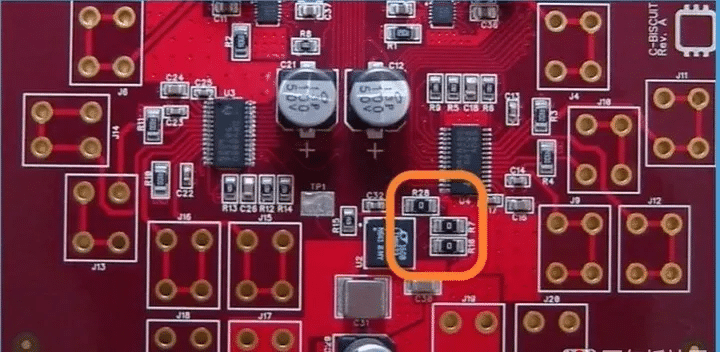
Choosing and Using 0 Ohm Resistors: Key Considerations
When it comes to choosing and using 0 Ohm Resistors in your electronic designs, there are several key considerations to keep in mind. These factors will ensure that you select the right resistor for your needs and use it effectively to achieve optimal performance and reliability.
Understanding Your Requirements
Before you even begin to consider specific 0 Ohm Resistors, it’s important to have a clear understanding of your requirements. What is the purpose of the resistor in your circuit? What are the operating conditions? Understanding these requirements will guide your selection process and ensure that the chosen resistor is fit for purpose. For example, if you’re designing a high-frequency circuit, you might need a 0 Ohm Resistor with a high-frequency performance.
Current Handling Capacity
One of the first factors to consider when choosing a 0 Ohm Resistor is its current handling capacity. The chosen resistor should be able to handle the maximum current expected in the circuit without exceeding its power rating or causing excessive heating. For instance, if your circuit operates at a current of 1A, you should choose a 0 Ohm Resistor that can handle at least this amount of current.
Power Dissipation
Power dissipation is another key consideration. All resistors generate heat when current flows through them, and 0 Ohm Resistors are no exception. It’s important to ensure that the power dissipated by the resistor does not exceed its rated power, even under maximum current conditions. For example, if your circuit operates at a power of 1W, you should choose a 0 Ohm Resistor that can dissipate at least this amount of power.
Tolerance and Accuracy
While 0 Ohm Resistors are intended to have negligible resistance, they do have some small resistance value due to manufacturing variations. If precise resistance values are critical in your application, you’ll need to consider the resistor’s tolerance and accuracy. For example, if your circuit requires a resistance accuracy of 1%, you should choose a 0 Ohm Resistor with a tolerance of 1% or better.
SMT Footprint and Assembly
The 0 Ohm Resistor you choose should have a suitable Surface Mount Technology (SMT) footprint that is compatible with your PCB design and assembly process. Be sure to double-check the recommended pad layout and soldering guidelines to avoid any assembly issues. For example, if your PCB design uses a 0603 SMT footprint, you should choose a 0 Ohm Resistor that fits this footprint.
Thermal Considerations
Thermal management is crucial when using 0 Ohm Resistors. The resistor should be adequately thermally connected to the PCB or surrounding components to dissipate any heat generated. Poor thermal management can lead to increased resistance and potential component failure. For example, you might need to consider using a heat sink or thermal vias to help dissipate heat.
PCB Layout and Traces
Finally, when placing 0 Ohm Resistors on your PCB, pay careful attention to signal paths, power distribution, and potential noise or interference concerns. Proper layout can help maintain signal integrity and reduce the risk of unintended coupling between traces. For example, you might need to consider the placement of the 0 Ohm Resistor in relation to other components and traces to avoid crosstalk or interference.
By keeping these considerations in mind, you can choose and use 0 Ohm Resistors effectively in your electronic designs, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Absolutely, I can incorporate that into the conclusion. Here’s the revised version:
Conclusion
The 0 Ohm Resistor, a seemingly simple component, is a silent workhorse in the realm of electronics. Its versatility and crucial role in various applications make it an indispensable part of any electronic design.
In essence, the humble 0 Ohm Resistor is not just a component; it’s a key to optimal performance and reliability in your designs.
At Rowsum, we’re committed to helping you bring your electronic designs to life with high-quality products and services tailored to your needs. We invite you to explore our services and see how we can support your electronic design journey:
For any inquiries or further information, feel free to reach out to us at [email protected].
FAQ
| Common Questions about 0 Ohm Resistors | Answers |
|---|---|
| What is a 0 Ohm Resistor? | A 0 Ohm Resistor is a passive two-terminal electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. It offers no resistance to the current flowing through it, acting like a straight wire. |
| Why use a 0 Ohm Resistor instead of a wire? | 0 Ohm Resistors are often used instead of wires for their compatibility with automated assembly processes, ease of modification, and ability to serve as placeholders or bridges in PCB layouts. |
| Can a 0 Ohm Resistor be used as a fuse? | Yes, in certain scenarios, a 0 Ohm Resistor can act as a fuse replacement to provide over-current protection. |
| Do 0 Ohm Resistors generate heat? | While 0 Ohm Resistors are designed to have negligible resistance, they can generate a small amount of heat due to their physical properties and the current flowing through them. |
| How do I choose the right 0 Ohm Resistor? | Choosing the right 0 Ohm Resistor involves understanding your specific needs and considering factors like current handling capacity, power dissipation, tolerance, and accuracy. |