Introduction to PCBs
Ever wondered what’s behind your smartphone’s intelligence or your laptop’s versatility? How does a tiny smartwatch pack so much functionality? The secret lies in a small but vital component: the Printed Circuit Board, or PCB.
PCBs are the lifeblood of all electronic devices. They connect all the components in a device, from tiny resistors to large microprocessors. But, PCBs come in various types, each with its unique characteristics and uses.
In this article, we’ll journey through the different types of PCBs, their features, and applications. Whether you’re an electronics enthusiast or just curious, this guide will offer valuable insights. Ready to dive into the fascinating world of PCBs?
The Importance of PCBs
PCBs are more than just electronic components; they’re the foundation of all the devices we use daily. Without them, our smartphones, laptops, and even appliances wouldn’t function. PCBs are the unsung heroes of the electronic world. Let’s delve deeper into their importance in the next section.
Understanding the Basics of PCB Design
Before we dive into the different types of PCBs, it’s essential to grasp the basics of PCB design. PCB design is a complex process that requires a deep understanding of electrical engineering and the ability to use specialized software.
A PCB is made up of several layers, including the substrate, copper, solder mask, and silkscreen. The substrate, usually made of fiberglass, provides the PCB with its rigidity. The copper layer contains the electrical circuits that connect the various components. The solder mask, usually green, insulates the copper circuits, preventing short circuits. Finally, the silkscreen layer contains labels for easier component identification.
PCB design starts with a schematic diagram, a blueprint of the electrical connections. This schematic is then converted into a layout, which maps the physical locations of the components on the PCB. The layout also includes the routing, which are the pathways that electrically connect the components.
PCB design is a balancing act between electrical requirements, physical constraints, and production costs. A well-designed PCB not only functions correctly but is also easy and cost-effective to manufacture. Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s explore the different types of PCBs.
The Different Types of PCBs
Now that we’ve covered the basics of PCB design, let’s delve into the different types of PCBs. Each type has its unique characteristics and applications, making it suitable for specific devices and uses. Understanding these differences is crucial when choosing the right PCB for your project.
Single-Sided PCBs
Single-sided PCBs are the simplest and most common type of PCB. They have components on one side of the board and a conductive pathway on the other. Single-sided PCBs are ideal for simple electronics like calculators and radios due to their simplicity and low cost.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Single-Sided PCBs
While single-sided PCBs are cost-effective and easy to manufacture, their simplicity also limits their complexity. They’re not suitable for complex devices with many components or circuits.
Double-Sided PCBs

Double-sided PCBs have components and conductive pathways on both sides of the board, allowing for more complex circuits. They’re used in more complex devices like power supplies and control relays. Double-sided PCBs offer more flexibility in design but are also more challenging to manufacture.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Double-Sided PCBs
Double-sided PCBs can accommodate more components and circuits, making them suitable for more complex devices. However, they require careful planning to avoid short circuits and are more expensive to produce.
Multilayer PCBs
Multilayer PCBs have multiple layers of substrate with conductive pathways, allowing for even more complex circuits. They’re used in highly complex devices like computers and medical equipment. Multilayer PCBs are the pinnacle of PCB design, offering high capacity in a compact size.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Multilayer PCBs
Multilayer PCBs can handle extremely complex circuits and high-speed circuits, making them ideal for advanced electronics. However, they’re the most expensive type of PCB to produce and require specialized equipment to manufacture.
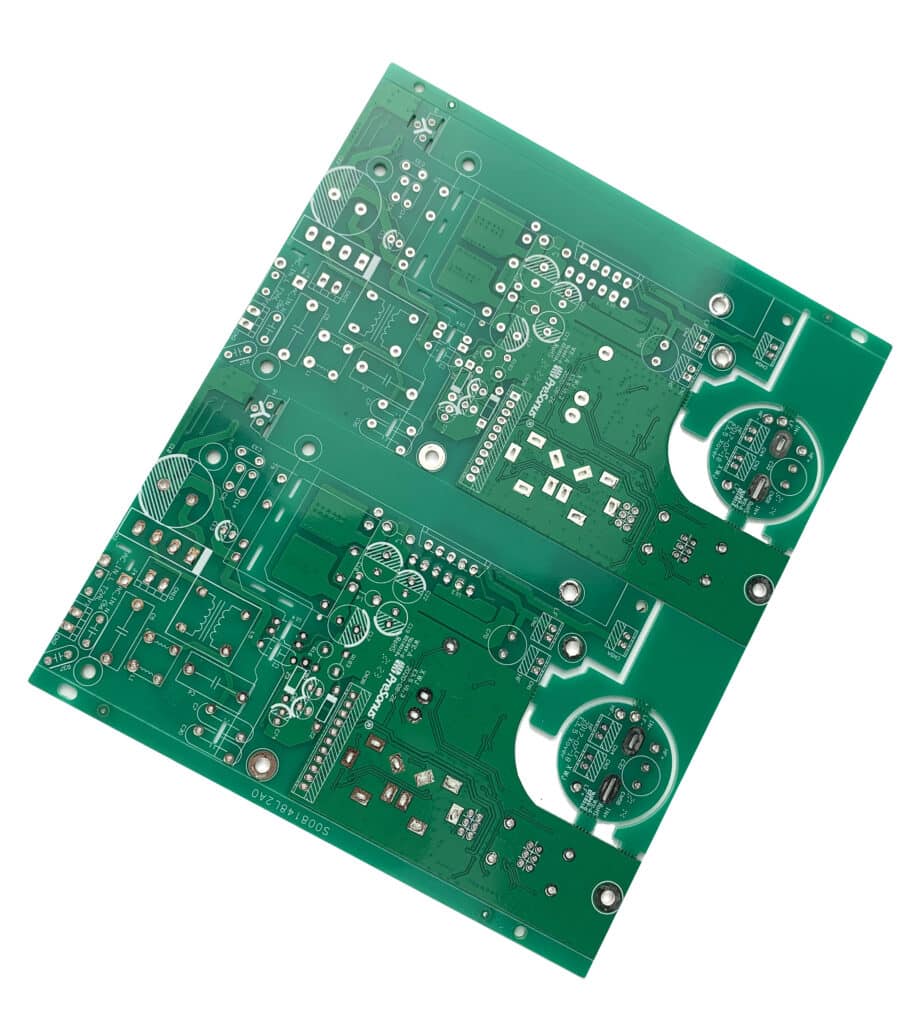
Rigid PCBs

Rigid PCBs are made from a solid substrate material that prevents the board from bending. They’re used in most electronics due to their durability and reliability. Rigid PCBs are the workhorse of the PCB world, providing a sturdy base for components.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rigid PCBs
Rigid PCBs are durable and reliable, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. However, their rigidity can be a disadvantage in devices that require flexibility.
Flex PCBs
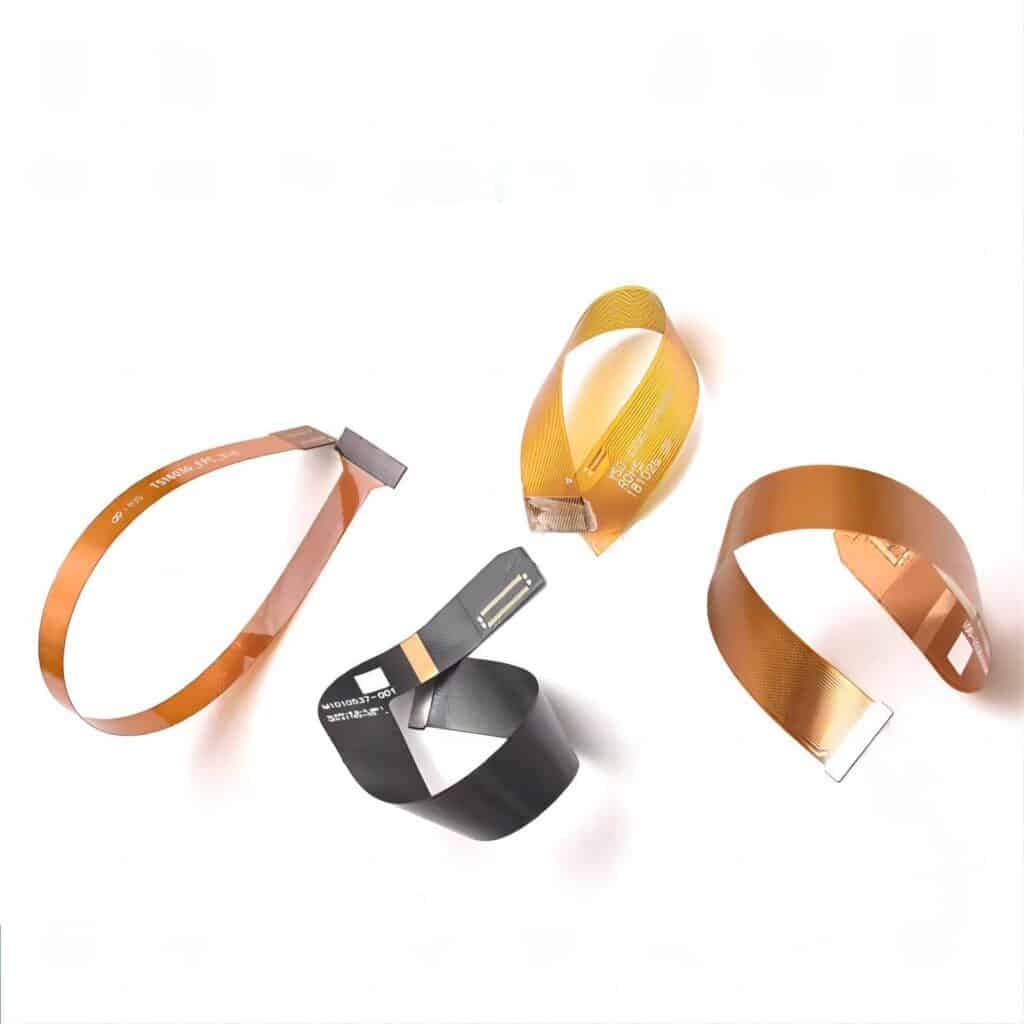

Flex PCBs are made from flexible materials, allowing the board to bend without damaging the circuits. They’re used in devices that require flexibility, like cameras and wearable devices. Flex PCBs bring a new level of versatility to PCB design.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Flex PCBs
Flex PCBs can bend and flex, making them ideal for devices that require flexibility. However, they’re more challenging to design and manufacture, and they can be more expensive than rigid PCBs.
Rigid-Flex PCBs
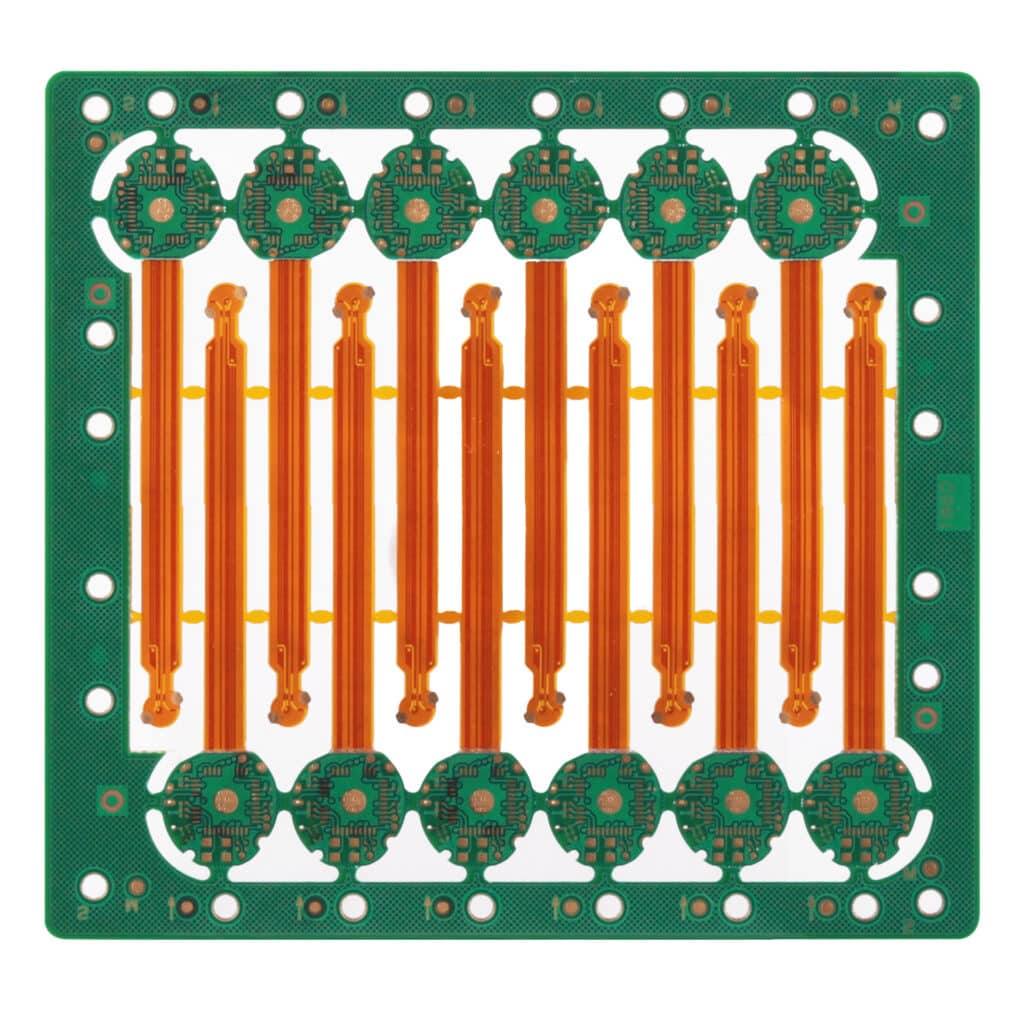
Rigid-flex PCBs combine the advantages of rigid and flex PCBs. They have flexible sections for bending and rigid sections for component mounting. Rigid-flex PCBs offer the best of both worlds, providing flexibility where needed and rigidity where required.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rigid-Flex PCBs
Rigid-flex PCBs offer a unique combination of flexibility and rigidity, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. However, they’re the most complex type of PCB to design and
manufacture, and they can be more expensive than other types of PCBs.
Understanding the different types of PCBs and their advantages and disadvantages can help you choose the right PCB for your project. Whether you need a simple single-sided PCB for a basic device or a complex multilayer PCB for advanced electronics, there’s a PCB type that fits your needs.
Choosing the Right Type of PCB
Selecting the appropriate PCB for your project is a pivotal decision. It’s not merely about the complexity of the circuits, but also about the physical constraints of the device, the production costs, and the intended use of the device. The right PCB can make the difference between a device that performs reliably and one that falls short.
Factors to Consider
When choosing a PCB, several factors come into play. Let’s delve deeper:
Complexity of the Circuits
The complexity of your circuits is a significant factor. For instance, if you’re designing a simple device like a digital thermometer or a basic LED lighting system, a single-sided PCB might suffice. It’s cost-effective and can easily handle the simple circuitry involved in these devices.
However, if you’re working on a more complex device, like a smartphone, a gaming console, or a high-performance computer server, a multilayer PCB is necessary. These devices require complex circuitry to handle multiple functions simultaneously, making multilayer PCBs a must.
Physical Constraints
The physical size and flexibility of your device also matter. If you’re designing a compact, flexible device like a fitness tracker, a smartwatch, or even a foldable smartphone, a flex PCB is the perfect choice. Flex PCBs can bend without damaging the circuits, making them ideal for devices that require flexibility.
On the other hand, if you’re creating a larger, stationary device like a desktop computer, a home security system, or an industrial control panel, a rigid PCB is more suitable. These PCBs are sturdy and can handle the weight of multiple components.
Durability Requirements
The durability of your PCB is another crucial factor. If your device will be used in harsh conditions, like an outdoor security camera, a drone, or a marine navigation system, a rigid or rigid-flex PCB might be the best choice. These PCBs are robust and can withstand challenging environments, ensuring your device continues to function reliably.
Production Budget
Lastly, consider your production budget. Single-sided PCBs are the most cost-effective, but they’re also the simplest. If your budget allows, and your project requires more complex circuitry, like a high-end audio amplifier, a sophisticated medical device, or a high-speed network router, double-sided or multilayer PCBs might be worth the investment. These PCBs can handle complex circuits, providing superior performance.
By considering these factors, you can choose a PCB that not only fits your device but also aligns with your business goals. Remember, the right PCB can enhance the performance of your device and contribute to its success.
Conclusion
PCBs are the backbone of all electronic devices, and understanding the different types of PCBs is crucial for anyone involved in electronics. Whether you’re a hobbyist building your first device or a professional designing advanced electronics, knowing the different types of PCBs and their advantages and disadvantages can help you make the right choices for your projects.
From simple single-sided PCBs for basic devices to complex multilayer PCBs for advanced electronics, there’s a PCB type that fits your needs. Consider the complexity of your circuits, the physical constraints of your device, the durability requirements, and your production budget to choose the right PCB.
Remember, the right PCB can enhance the performance of your device and contribute to its success. So, whether you’re designing a digital thermometer, a high-performance computer server, a foldable smartphone, or a high-speed network router, choose your PCB wisely. Your choice of PCB can make or break your device.
FAQs
- What is a PCB?
A PCB, or Printed Circuit Board, is a board that connects the components of an electronic device. - What are the different types of PCBs?
There are several types of PCBs, including single-sided, double-sided, multilayer, rigid, flex, and rigid-flex PCBs. - What type of PCB is right for my project?
The right type of PCB for your project depends on the complexity of the circuits, the physical constraints of the device, the durability requirements, and the production budget. - What are the advantages and disadvantages of different types of PCBs?
Each type of PCB has its advantages and disadvantages. For example, single-sided PCBs are simple and cost-effective but limited in complexity, while multilayer PCBs can handle complex circuits but are more expensive to produce. - Where can I get PCBs for my project?
You can get PCBs from a PCB manufacturer like Rowsum, which specializes in high-quality PCB products and offers excellent customer service.
Get Access Now: www.rowsum.com