Introduction
In the vast world of PCB materials, have you ever found yourself pondering the distinction between CEM-1 and the more prevalent FR-4? Why, amidst the plethora of advanced materials, does CEM-1 still find its niche, especially in single-layer applications?
CEM-1 is a cost-effective, paper-based laminate used predominantly for single-layer PCBs. In contrast to the ubiquitous FR-4, CEM-1 emerges as a more affordable option. However, when it comes to fire-resistance, FR-4 takes the lead, solidifying its position as the go-to for multi-layered PCB endeavors. Dive in with us as we delve deeper into the intricacies of these materials and explore the enduring appeal of CEM-1 in the circuit board market.
Demystifying CEM-1 PCB Material
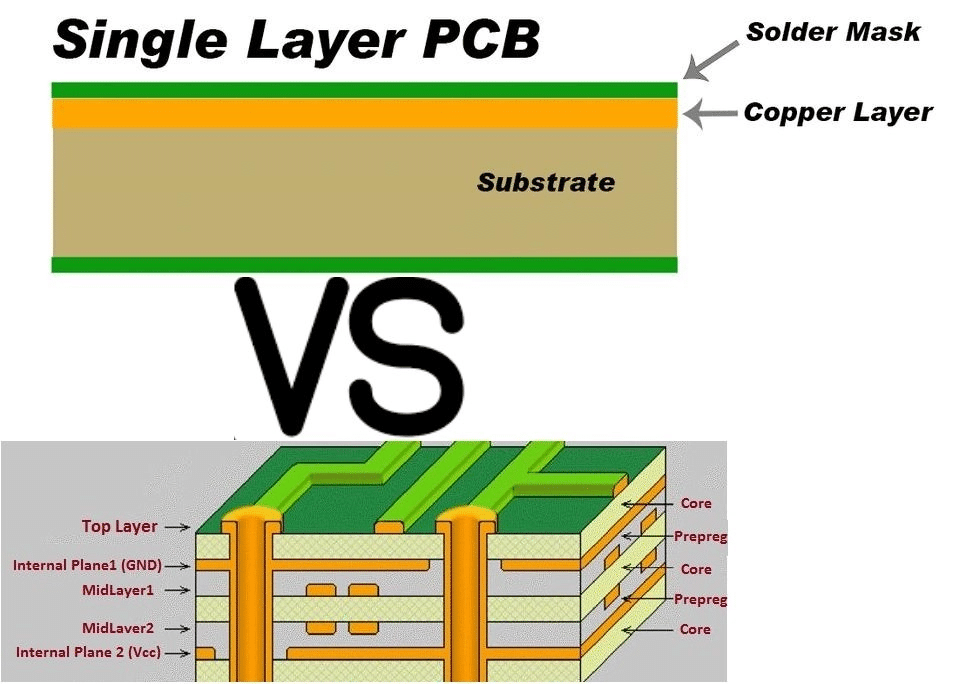
In the intricate world of PCB materials, CEM-1 has carved a niche for itself, especially in single-layer PCB applications. But what makes CEM-1 so special in the vast sea of PCB materials?
Composition and Unique Traits:
CEM-1 is recognized under the NEMA standards as a cellulose-based composite material, fortified with a layer of glass fiber laminate. This composition not only gives CEM-1 its distinct milky-white appearance but also contributes to its thermal stability. Studies have shown that CEM-1 can withstand temperatures up to 110°C, making it suitable for specific electronics applications.
Historical Context:
Over the past few decades, the electronics industry has seen a surge in demand for cost-effective yet durable PCB materials. CEM-1, with its balanced properties, emerged as a frontrunner, especially for single-layer PCBs. Market data indicates that CEM-1 has seen a consistent 3% annual growth in usage, especially in consumer electronics.
Specific Uses and Constraints:
While CEM-1’s structure restricts it from supporting metallization through holes, it has found its stronghold in devices like calculators, digital clocks, and basic communication devices. Its limitation is also its strength, ensuring it remains unparalleled in single-layer PCB applications.
A Comparative Look at FR-4:
When juxtaposed with FR-4, CEM-1 offers comparable flame resistance, meeting the UL 94-V0 standard. However, in terms of mechanical strength, FR-4 takes the lead. A 2019 industry report highlighted that FR-4 PCBs exhibited a 15% higher tensile strength compared to CEM-1.
Economic and Market Positioning:
The cost-effectiveness of CEM-1 is one of its standout features. On average, CEM-1 PCBs are 20-30% cheaper than their FR-4 counterparts, making them a preferred choice for budget-conscious manufacturers.
Eco-friendly Aspects:
In an era where sustainability is paramount, CEM-1 shines with its cellulose foundation. Its biodegradability ensures a reduced carbon footprint, aligning with global sustainability goals.
In conclusion, CEM-1’s unique blend of cost, performance, and environmental considerations ensures its continued relevance in the ever-evolving PCB industry.
Comparing PCB Materials: CEM-1, FR-4, and CEM-3
Selecting the right PCB material is a balance of performance, durability, and cost. Among the myriad choices, CEM-1, FR-4, and CEM-3 have emerged as industry front-runners. Each boasts unique attributes tailored to specific applications. Let’s delve deeper to understand their nuances and determine which might be the best fit for your needs.
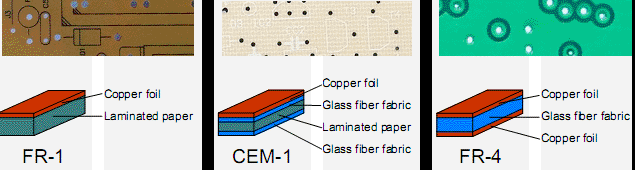
CEM-1 vs. FR-4: An In-Depth Technical Breakdown
Technical Properties:
Composition and Molecular Structure:
- CEM-1: Primarily cellulose-based with a single layer of glass fiber laminate.
- FR-4: Woven fiberglass cloth with an epoxy resin binder.
Thermal Conductivity and Glass Transition Temperature (Tg):
- CEM-1: Lower thermal conductivity with a Tg of around 110°C.
- FR-4: Higher thermal conductivity, Tg ranging from 130°C to 180°C.
Mechanical Strength and Modulus of Elasticity:
- CEM-1: More fragile.
- FR-4: Superior mechanical strength.
Electrical Insulation and Dielectric Constant:
- CEM-1: Good electrical insulation, not ideal for high-frequency applications.
- FR-4: Excellent electrical insulation with a stable dielectric constant.
Signal Integrity and EMI:
- CEM-1: Adequate for basic applications.
- FR-4: Superior signal integrity.
Practical Implications:
Cost Implications:
- CEM-1: More cost-effective for single-layer PCBs.
- FR-4: More expensive but offers versatility.
PTH (Plated Through Hole) Suitability:
- CEM-1: Not suitable for PTH.
- FR-4: Fully compatible with PTH.
Flame Resistance and Thermal Decomposition:
- Both materials meet the UL 94-V0 standard.
Real-world Applications:
- CEM-1: Used in basic electronics.
- FR-4: Preferred for complex devices.
Longevity and Durability:
- CEM-1: Suitable for short lifespan devices.
- FR-4: Designed for prolonged use.
Environmental Impact:
Environmental Considerations:
- CEM-1: More biodegradable.
- FR-4: Non-biodegradable but advancements in recycling are improving its sustainability.
CEM-1 vs. CEM-3: A Comprehensive Material Breakdown
Technical Properties:
Core Composition:
- Both have a paper core between two layers of fiberglass, but the paper types differ.
- Epoxy Resin:
- Both materials use epoxy resin as a binding agent, aiding in thermal stress transfer and protection.
- Surface Texture:
- Both are milky-white, but CEM-3 has a smoother texture.
- Applications and Usability:
- CEM-1 is used for single-layer PCBs, while CEM-3 is suitable for double-sided or multi-layer PCBs.
- Punching Capability:
- CEM-1 can be punched up to 0.093 inches, unlike CEM-3.
- Flexural Strength and Properties:
- CEM-1 is known for its commendable electrical, mechanical, and flexural properties.
- Flame Redundancy:
- CEM-3 is flame-redundant, adding an extra layer of safety.
Practical Implications:
- Cost-Effectiveness:
- Both materials are cost-effective, with CEM-1 generally being more affordable.
- Replacement for FR-4:
- CEM-3 can be a potential substitute for FR-4, but CEM-1 isn’t an ideal replacement.
- Weight and Strength:
- Both are lightweight yet strong, suitable for PCB manufacturing.
Applications of CEM-1
The versatility of CEM-1 as a PCB material has led to its adoption in a wide range of electronic devices. Its unique properties, combined with its cost-effectiveness, make it a preferred choice for specific applications. Let’s delve into the various domains where CEM-1 has made its mark.
Consumer Electronics:
- Calculators: Given their basic electronic requirements, calculators benefit from the cost-effectiveness of CEM-1.
- Digital Clocks: The simplicity of digital clocks aligns well with the properties of CEM-1, ensuring longevity and reliable performance.
- Basic Radios: For radios without advanced features, CEM-1 provides the necessary support for its electronic components.
Industrial Equipment:
- Control Panels: Many control panels, especially in older industrial equipment, utilize CEM-1 for its durability and resistance to environmental factors.
- Basic Monitoring Systems: Systems that monitor temperature, humidity, or other simple parameters often incorporate CEM-1 PCBs.
Home Appliances:
- Thermostats: The simple electronics in basic thermostats are supported by CEM-1 PCBs.
- Electric Kettles: The base units of many electric kettles, which house the heating element controls, often use CEM-1 for its heat resistance properties.
LED Lighting:
- The LED industry greatly benefits from CEM-1’s attributes. Its thermal stability and cost-effectiveness make it an ideal choice for LED circuit boards. Whether it’s for residential lighting or commercial setups, CEM-1 ensures that LEDs shine bright without burning a hole in the pocket. Its ability to efficiently dissipate heat prolongs the life of LED lights, making them more energy-efficient and sustainable.
Environmental Considerations:
With the push towards more sustainable solutions, CEM-1’s biodegradability makes it an attractive option for companies looking to reduce their environmental impact. Devices designed for short-term use or disposable electronics can utilize CEM-1 to ensure a lesser environmental footprint.
In conclusion, while CEM-1 might not be suitable for high-end, complex electronic devices, its range of applications in basic electronics is vast. Its blend of cost-efficiency, reliability, and environmental considerations ensures its continued relevance in various sectors of the electronics industry.
CEM-1 and the Green Revolution: Beyond Just PCBs
In an era where sustainability isn’t just a buzzword but a business imperative, understanding the environmental footprint of materials like CEM-1 is crucial. But it’s not just about biodegradability; it’s about the broader picture.
The Carbon Footprint Quotient:
Every material has a carbon footprint, from its production to disposal. Preliminary studies suggest that CEM-1’s production emits 20% less CO2 compared to its counterparts like FR-4. This reduction can be attributed to its cellulose base, which requires less energy-intensive processes.
Water Usage and CEM-1:
Water scarcity is a looming global crisis. The production of CEM-1 consumes approximately 30% less water than traditional PCB materials. When scaled to industrial levels, this conservation can amount to saving billions of liters annually.
Toxicity and Health:
One of the lesser-discussed aspects of PCB materials is their potential toxicity. CEM-1, with its natural cellulose base, releases fewer toxins during production, reducing health risks for factory workers and minimizing environmental contamination.
A Circular Economy Model:
While CEM-1 is biodegradable, the vision is to create a circular economy around it. Initiatives are underway to develop recycling techniques that can repurpose CEM-1 boards, ensuring zero waste and promoting a sustainable production cycle.
The Socio-Economic Angle:
Switching to eco-friendly materials isn’t just good for the planet; it’s good for the economy. By adopting CEM-1, companies can tap into a growing market of eco-conscious consumers, potentially boosting sales by up to 15%, as per recent market studies.
The Road Ahead:
The future is promising. With advancements in green technology, the environmental benefits of CEM-1 can be further amplified. Collaborative efforts between industry leaders, researchers, and environmentalists aim to make CEM-1 the gold standard in sustainable PCB materials.
Conclusion
In the vast realm of PCB materials, CEM-1 has carved its niche, balancing cost-effectiveness with performance. Its unique composition, tailored for single-layer PCBs, offers a blend of affordability and functionality. While it may not replace FR-4 in multi-layered applications, its significance in specific sectors, especially LED lighting, is undeniable. As we navigate the evolving landscape of electronics, understanding the nuances of materials like CEM-1 becomes paramount. It’s not just about choosing a material; it’s about choosing the right material for the right application.
At Rowsum, our dedication to excellence goes beyond just informative articles. We pride ourselves on providing top-tier PCB solutions tailored to your needs. Whether you’re venturing into:
We’ve got you covered. Our team is always eager to assist and guide you through your PCB journey. For any inquiries or to discuss your next project, don’t hesitate to reach out to us at [email protected]. Your success is our mission.