Introduction
Have you ever tried identifying a specific SMD component on a circuit board and felt lost? Or wondered about the different types of SMD components and their specific applications?As the world of electronics evolves towards compactness and sophistication, grasping the nuances of Surface Mount Devices (SMD) becomes imperative for professionals, enthusiasts, and the general public alike.
At the core of this miniaturization trend lies SMD technology. SMD components are tiny electronic components that are affixed directly to the surface of PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards). They play a pivotal role in modern electronics, enabling devices to be more streamlined without sacrificing functionality. This guide will delve deep into the world of SMD components, helping you identify, understand, and utilize them effectively.
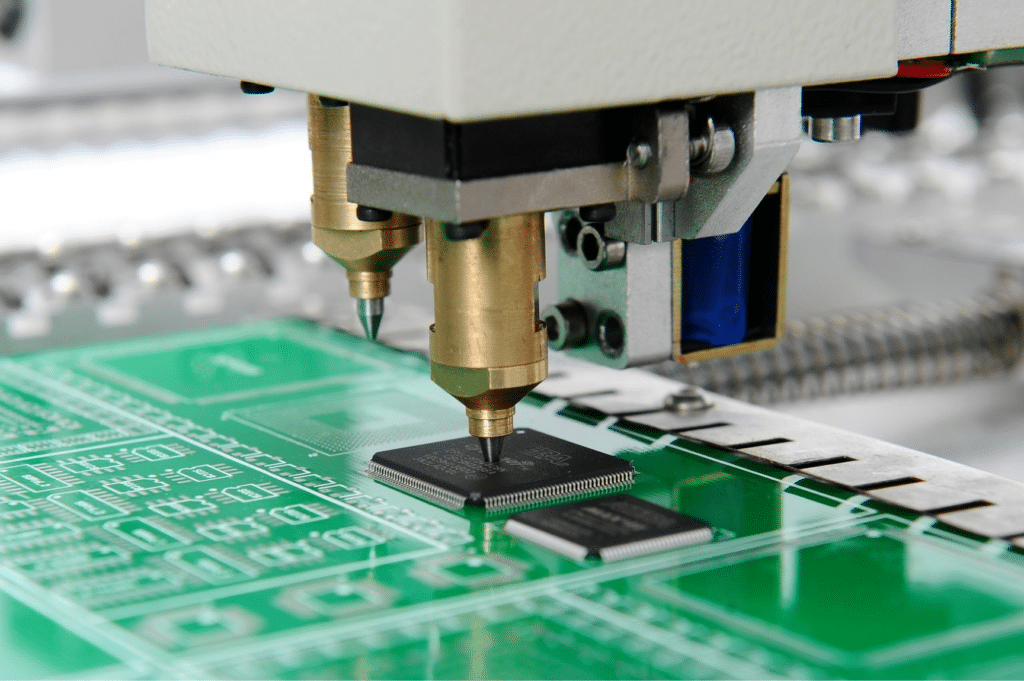
What Are SMD Components?
Definition and Basics
Surface Mount Devices, abbreviated as SMD components, signify a revolutionary shift in the realm of electronic component architecture. Contrary to conventional components that use leads penetrating through board holes, SMD components are positioned atop the circuit board. This shift in design not only changed the physical appearance of components but also introduced new manufacturing techniques and considerations. As we navigate the realm of SMDs, it’s vital to comprehend the fundamental principles that set them apart from earlier components and discern their impact on the contemporary electronics scene.
The Evolution of SMD Technology
It’s fascinating to think that while SMD components have their roots in the 1960s, it wasn’t until the vibrant tech boom of the 1980s that they truly found their place in mainstream electronics. As the demand for smaller, more portable electronic devices grew, the limitations of traditional through-hole components became evident. Their long leads and larger sizes were becoming less practical for the evolving needs of the industry. SMD technology emerged in response, offering a more compact and efficient solution that would shape the future of electronics.
Key Characteristics of SMD Components
- Size: One of the first things you’ll notice about SMD components? Their size. They’re impressively compact compared to traditional components. This isn’t just for aesthetics; it allows for a much denser arrangement on a PCB.
- Flexibility: Their design allows SMD components to be placed on both sides of a PCB, facilitating more intricate circuit designs.
- Durability: With fewer external leads and a direct mount to the PCB, SMD components tend to be more robust and reliable.
Benefits of Implementing SMD Technology
Moving from traditional through-hole components to Surface Mount Devices (SMDs) wasn’t merely a design tweak. It felt like a seismic shift, ushering in a wave of benefits that turned the electronics industry on its head. Let’s explore the key benefits of using SMD components:
Miniaturization and High Density
A standout benefit of SMD components is their notably small footprint. This miniaturization allows for a higher component density on a PCB, meaning more components can fit into a smaller space. As devices become more sophisticated, the ability to pack more functionality into a compact form factor becomes invaluable.
Improved Performance and Reliability
SMD components often result in faster signal transmission due to shorter interconnections. This leads to enhanced performance, especially in high-frequency applications. Additionally, with fewer external leads and direct mounting, there’s a reduced risk of connection issues, ensuring a more reliable final product.
Cost-Effective Production
The streamlined design of SMD components simplifies the manufacturing process. Automated machines can place these components more rapidly than traditional ones, leading to faster production times and reduced labor costs. This efficiency translates to cost savings for manufacturers and, ultimately, consumers.
Enhanced Thermal Performance
SMD components generally have better heat dissipation properties. Their design allows for a more direct thermal connection to the PCB, ensuring that heat is dispersed more effectively, which is crucial for maintaining the longevity and performance of electronic devices.
Design Flexibility
The ability to place SMD components on both sides of a PCB offers designers greater flexibility. This dual-sided placement facilitates more intricate and innovative circuit designs, allowing for the creation of more advanced electronic devices.
Reduced Weight
Given their compact nature, SMD components contribute to a significant reduction in the overall weight of electronic devices. This is especially beneficial for portable gadgets where every gram counts.
Incorporating SMD components into electronic designs offers a myriad of advantages, from cost savings to enhanced performance. With the relentless march of technology, the role of these components in molding the future of electronics is undeniable.
SMD Components vs. Through-Hole Components

The electronics industry has seen a significant shift from the traditional through-hole components to the more modern Surface Mount Devices (SMDs). Both have their unique advantages and applications. Let’s explore the differences between the two and understand when and why one might be preferred over the other.
Definition and Design
Through-Hole Components: These are components where leads are threaded through specific holes made in the PCB. Once inserted, they are attached via soldering to the pads located on the other side. This design provides a strong physical bond, making them ideal for applications where the component may undergo mechanical stress.
SMD Components: As previously discussed, SMD components are designed to be placed directly onto the surface of PCBs. They don’t require drilled holes, leading to a more streamlined manufacturing process and allowing for dual-sided component placement.
Size and Weight
Through-Hole Components: Generally larger in size, these components can contribute to a bulkier and heavier final product.
SMD Components: Their sleek structure facilitates tighter component arrangement, leading to a more lightweight final product, a key aspect for mobile gadgets.
Performance and Frequency
Through-Hole Components: Due to their longer leads and the nature of their connection, they might not be ideal for high-frequency applications where signal speed and integrity are paramount.
SMD Components: SMD Components: Due to their brief interconnects, they ensure rapid signal relay, rendering them apt for tasks requiring high frequency.
Durability and Maintenance
Through-Hole Components: Their strong physical bond to the PCB makes them more durable against mechanical stresses. However, they can be more challenging to replace if a component fails.
SMD Components: While they offer a robust connection, extreme mechanical stress might pose challenges. On the upside, with the right equipment, they can be easier to replace or rework.
Cost and Manufacturing
Through-Hole Components: The need for drilling holes can increase manufacturing time and costs. They also typically require manual placement, further adding to production time.
SMD Components: Their design allows for automated placement, speeding up the manufacturing process and potentially reducing costs.
Application and Use Cases
Through-Hole Components: Ideal for prototypes and products where durability under mechanical stress is a priority. They’re also commonly found in power circuits and connectors.
SMD Components: Favored for bulk production, miniaturized gadgets, and tasks that demand high-frequency operations. Their versatility has made them a staple in modern electronics.
In conclusion, while SMD components have become the industry standard for many applications due to their numerous advantages, through-hole components still hold their ground in specific scenarios. The selection often hinges on the distinct needs of a given project.
Types of SMD Components
While SMDs have significantly impacted the electronics industry with their compactness and efficiency, it’s essential to recognize the diversity within this category. Various SMD components cater to a range of needs and applications. Let’s delve into some of the predominant varieties:
Passive SMD Components
These components do not have the ability to amplify signals or energy. They include:
- SMD Resistors: They act to counteract or confine electrical current flow. They are available in multiple dimensions, notably 0402, 0603, 0805, and 1206. They’re essential for biasing and filtering in circuits.
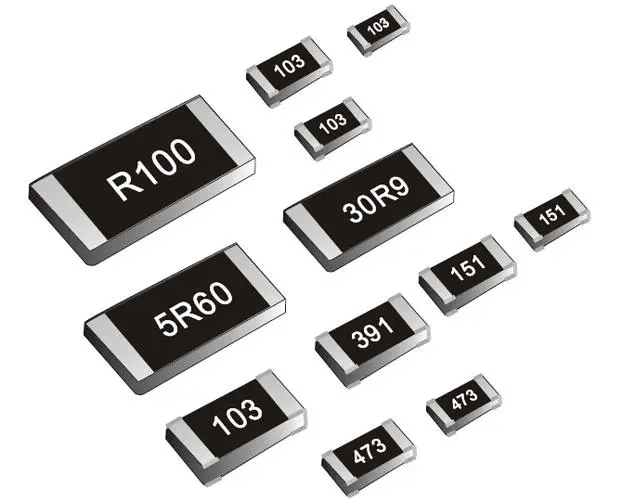
- SMD Capacitors: These capacitors, made from materials such as ceramic, tantalum, and polyester, function to accumulate and discharge electrical power. They play crucial roles in filtering and timing circuits.
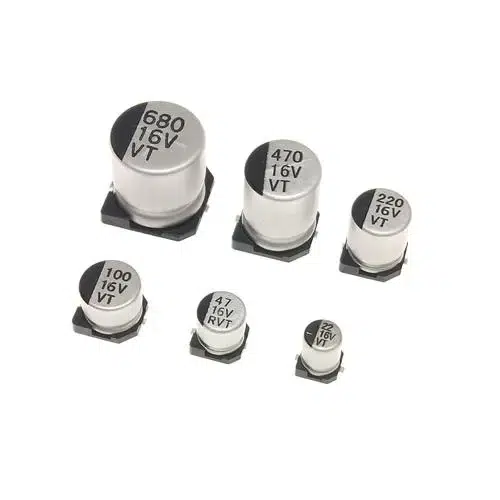

- SMD Inductors: They conserve energy in the form of a magnetic field when they experience current passage. Typically used in RF applications and power supply circuits.
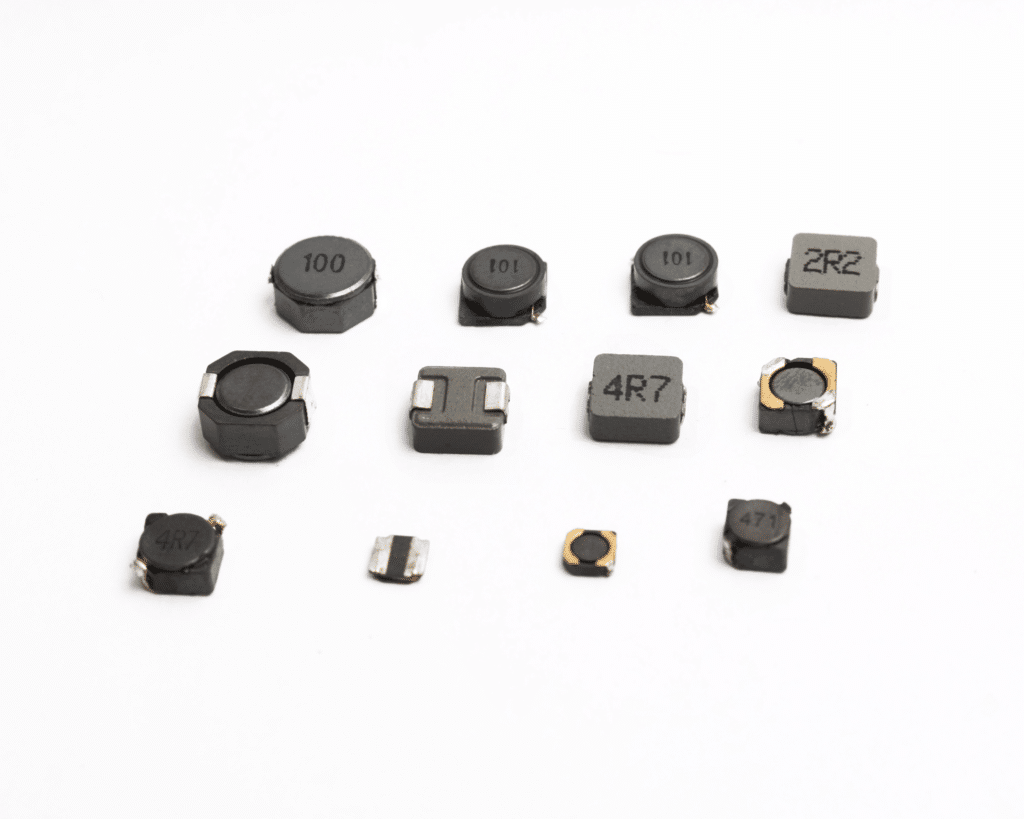
Active SMD Components
These components can amplify signals or energy. They include:
- SMD Diodes: SMD Diodes allow electrical current to flow in one specific direction. They are commonly used in voltage regulation, signal demodulation, and power conversion.
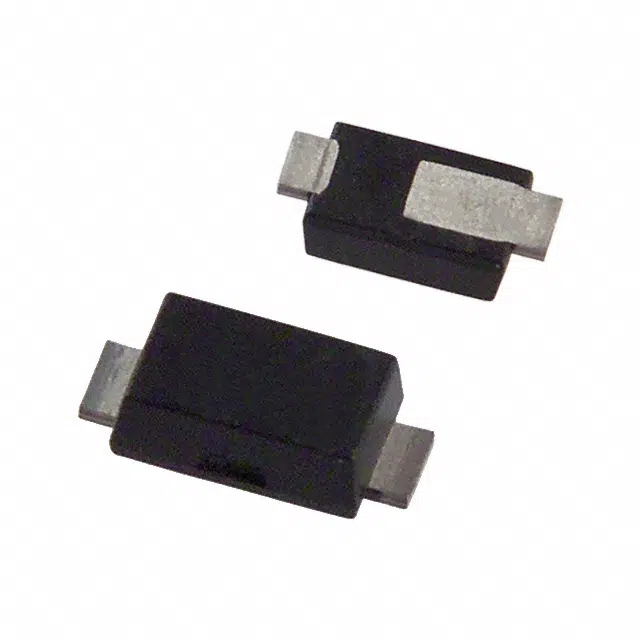

- SMD Transistors: Devices in the semiconductor category that boost or toggle electronic signals. Types include BJT and FET.
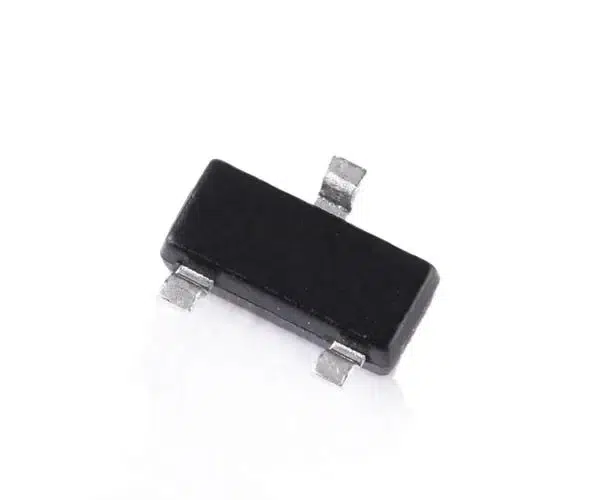

- SMD Integrated Circuits (IC): They are conglomerates of several components housed within one unit, facilitating intricate operations.
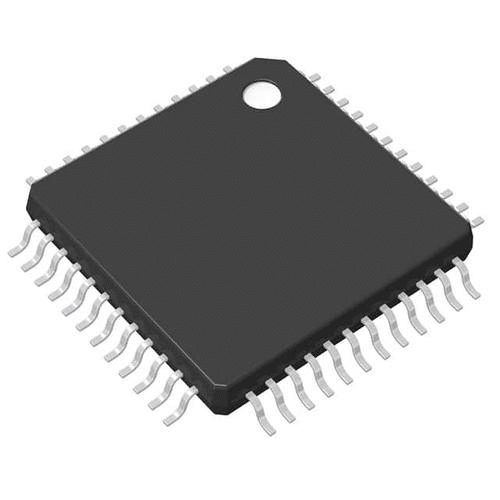
- SMD LEDs: Emit light when current flows through them.
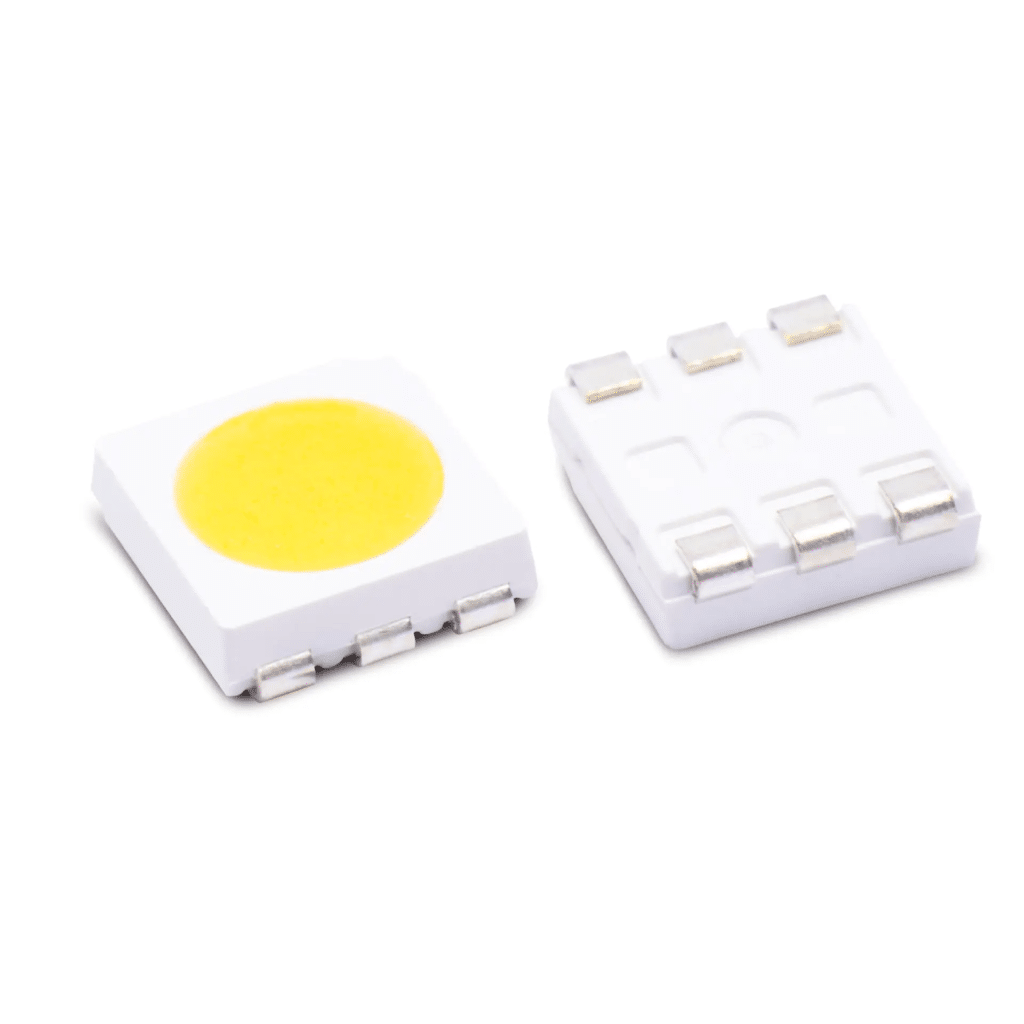

- SMD Oscillators: Generate repetitive waveforms, crucial for signal processing and synchronization.
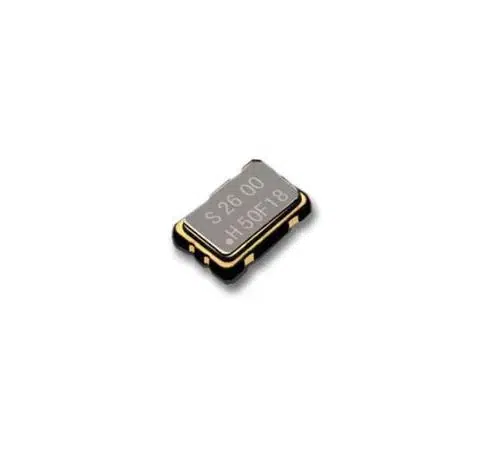

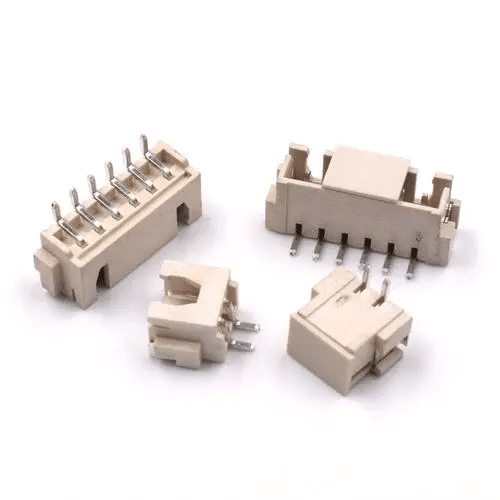
- SMD Connectors: Join sections of circuits together, including types like USB, HDMI, and SIM card slots.
| Component Type | Unit | Packaging | Typical Values | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resistor | Ohm (Ω) | 0402, 0603, 0805 | 1Ω – 10MΩ | Biasing, Filtering |
| Capacitor | Farad (F) | 0402, 0603 | 1pF – 1000μF | Filtering, Timing |
| Inductor | Henry (H) | 0402, 0603 | 1nH – 100mH | RF circuits, Power supplies |
| Diode | Volt (V), Ampere (A) | SOD-123, SOD-323 | 1V – 100V | Rectification, Protection |
| Transistor | Volt (V), Ampere (A) | SOT-23, SOT-223 | Varies | Amplification, Switching |
| IC | Varies | SOIC, QFP | Varies | Data processing, Power management |
| LED | Volt (V), Milliampere (mA) | 0603, 0805 | 1.8V – 3.3V | Display, Indication |
(Note: The values in the table are typical examples and can vary based on the specific component and manufacturer.)
Component Handling, Storage, and Other Considerations
Considering the vulnerability of SMD components to elements such as moisture, it’s paramount to house them in moisture-resistant packaging. They also come in various packaging types like Chip, SOP, QFP, and BGA. Each component has specific tolerances, power ratings, and temperature coefficients that influence its performance and application.
Choosing Quality SMD Components: A Personal Touch
Choosing the right SMD components extends beyond just the specifications. It’s about understanding the nuances, the little details that can make or break your project. Here’s a personal touch on what to keep in mind:
- Know Your Specs: It’s essential to be clear on the specifications and parameters of the components you’re sourcing. This ensures compatibility and optimal performance in your projects.
- Reliability Over Price: While cost is a factor, never compromise on quality. A slightly more expensive component that’s reliable can save you costs in the long run.
- Ask Questions: If in doubt, ask. Whether it’s about the component’s origin, its compatibility, or its performance under specific conditions, it’s better to be sure than sorry.
Choosing the Right Partner: Why Rowsum?

Navigating the world of SMD components requires a partner that not only understands the intricacies but also has the resources to deliver. Here’s why Rowsum is your ideal choice:
- Deep Expertise: With years of specialization, Rowsum’s expertise in the electronics industry is unparalleled. Our knowledge ensures you get the best advice and components for your projects.
- Direct Factory Access: Being a factory, we eliminate middlemen, ensuring you get the best prices and direct quality control.
- 1-on-1 Dedicated Service: Every client is paired with a dedicated specialist, ensuring personalized attention to your unique needs and swift responses to any queries.
- Reliable Component Sourcing: Our vast and dependable network means we can source a wide range of components, even in bulk, meeting almost any requirement you might have.
Embark on your next electronics venture with confidence. Discover the Rowsum difference at Rowsum.com. For inquiries or to get started, reach out to us at [email protected].
Conclusion
Within the expansive domain of contemporary electronics, SMD components emerge as cornerstone elements. They’re more than just tiny parts; they’re the essence of countless devices we depend on. As we’ve explored their diverse types, practical applications, and the nuances of selection, the significance of these components becomes undeniable. In the world of electronics, understanding the intricacies of SMDs can be the key to unlocking innovation and efficiency. Always remember, the right component can truly make all the difference.