Introduction to LED PCBs
Imagine you’re walking through a bustling city at night. The streets are illuminated by a myriad of lights, from the bright neon signs of shops to the soft glow of street lamps. As you marvel at the spectacle, have you ever stopped to wonder what makes all these lights possible? The answer lies in a small, yet powerful component: the LED PCB.
An LED PCB, or Light Emitting Diode Printed Circuit Board, is a specialized board designed to host and power LEDs. It provides a stable surface for LED placement and plays a crucial role in managing the heat generated by LEDs. This ensures optimal performance and longevity of LED lighting systems, making LED PCBs a key component in modern, energy-efficient lighting solutions.
An LED PCB is the heart of any LED lighting system. It’s where the LED components are mounted and electrically connected to create a functional lighting unit. But what exactly is an LED PCB, and how does it work? In this article, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of LED PCBs, exploring their components, types, advantages, and much more. Whether you’re a seasoned electronics professional or a curious beginner, this comprehensive guide will shed light on the intricate world of LED PCBs. So, let’s get started!
The Science Behind LED PCBs
Before we delve into the specifics of LED PCBs, it’s important to understand the science behind them. At the heart of an LED PCB is the Light Emitting Diode (LED) itself. LEDs are semiconductor devices that emit light when an electric current passes through them. This process is known as electroluminescence.
In an LED, the light is produced within the semiconductor material. When the electric current passes through the LED, it excites the electrons within the semiconductor. As these excited electrons return to their normal state, they emit photons – particles of light. The color of the light emitted by an LED depends on the type of semiconductor material used.
Now, let’s talk about the Printed Circuit Board (PCB). A PCB is a thin board made of insulating material, with conductive tracks printed or etched onto it. These tracks connect different electronic components mounted on the PCB, allowing electric current to flow between them. In an LED PCB, the LEDs are one of the key components mounted on the board.
The LED PCB not only provides a physical base for the LEDs but also plays a crucial role in heat dissipation. LEDs generate heat when they’re in operation, and this heat needs to be effectively managed to prevent damage to the LEDs and ensure their longevity. Many LED PCBs are made from materials like aluminum, which are excellent at dissipating heat.
In the next sections, we’ll delve deeper into the components of an LED PCB, the different types of LED PCBs, and their advantages. Stay tuned!
Types of LED PCBs
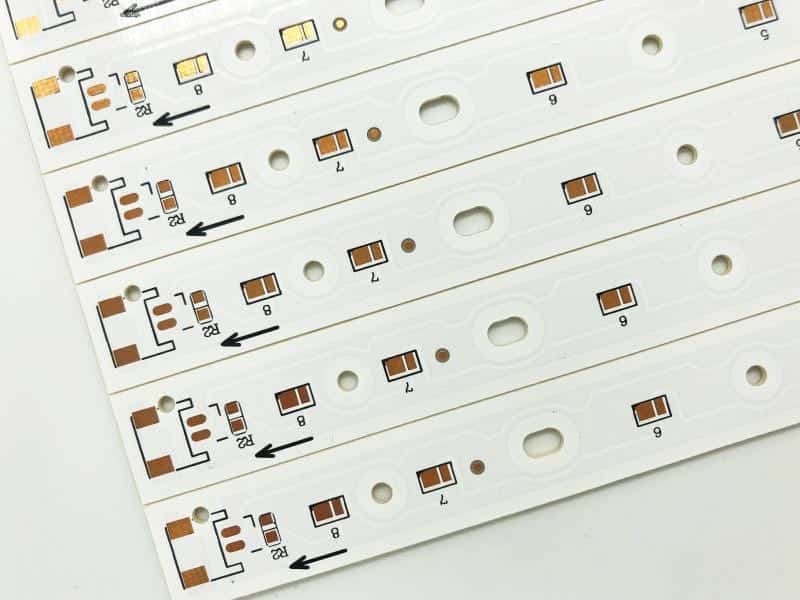

When it comes to LED PCBs, there are several types to choose from, each with its own unique features and advantages. Let’s take a closer look at some of the most common types of LED PCBs:
1. Single-Layer LED PCBs
Single-layer or single-sided LED PCBs are the simplest type of PCB. They have a single layer of substrate or base material, onto which the conductive material is printed. The LED components are then mounted onto this conductive layer. Single-layer LED PCBs are cost-effective and easy to manufacture, making them a popular choice for simple LED applications.
2. Double-Layer LED PCBs
Double-layer or double-sided LED PCBs have conductive layers on both sides of the substrate. This allows for more complex circuits, as components can be mounted on both sides of the PCB, and the two sides can be connected using through-hole technology. Double-layer LED PCBs are used in more complex LED applications where space is at a premium.
3. Multilayer LED PCBs
Multilayer LED PCBs have multiple layers of conductive material, separated by insulating layers. These PCBs can have anywhere from four to twelve layers, or even more in some cases. Multilayer LED PCBs allow for highly complex and compact circuits, making them ideal for advanced LED applications.
4. Aluminum LED PCBs
Aluminum LED PCBs are a special type of PCB designed for high heat dissipation. They have a thin layer of thermally conductive dielectric material that can transport and dissipate the heat from the LED to the aluminum board. Aluminum LED PCBs are widely used in LED lighting products due to their excellent heat dissipation capabilities.
5. Rigid LED PCBs
Rigid LED PCBs are made from a solid substrate material like fiberglass that prevents the board from bending. They are durable and easy to manufacture, making them a popular choice for a wide range of LED applications.
6. Flexible LED PCBs
Flexible LED PCBs are made from a flexible substrate material like flexible plastic or polyimide. They can be bent and flexed without damaging the circuit. Flexible LED PCBs are used in LED applications where the PCB needs to conform to a particular shape, such as in LED strips.
Each type of LED PCB has its own advantages and is suited to different types of LED applications. In the next section, we’ll delve deeper into the advantages of LED PCBs.
Advantages of LED PCBs
LED PCBs come with a host of advantages that make them an excellent choice for a wide range of applications. Here are some of the key benefits of using LED PCBs:
1. High Efficiency: LEDs are known for their high efficiency, and LED PCBs are no exception. They provide excellent luminous efficacy, with some LEDs producing up to 100 lumens per watt. This is significantly higher than traditional incandescent bulbs, which typically produce around 15 lumens per watt. This makes LED PCBs a cost-effective choice for a wide range of lighting applications.
2. Excellent Heat Dissipation: As mentioned earlier, many LED PCBs are made from materials like aluminum that are excellent at dissipating heat. This helps to manage the heat generated by the LEDs, ensuring their longevity and reliability. In fact, aluminum PCBs can dissipate heat up to 10 times faster than standard PCBs.
3. Compact and Lightweight: LED PCBs are compact and lightweight, making them ideal for applications where space is at a premium. Despite their small size, they can support a high number of LEDs, making them a powerful lighting solution.
4. Versatility: LED PCBs can be designed to fit a wide range of applications, from simple indicator lights to complex industrial lighting systems. They can also be made in a variety of shapes and sizes to fit specific requirements.
5. Durability: LED PCBs are highly durable and resistant to many common environmental factors, such as heat, cold, and vibration. This makes them a reliable choice for a wide range of applications.
6. Long Lifespan: LEDs are known for their long lifespan, with many LEDs lasting up to 50,000 hours or more. LED PCBs help to further extend this lifespan by providing effective heat management and a stable environment for the LEDs.
7. Environmentally Friendly: LEDs are more environmentally friendly than many traditional forms of lighting, as they consume less power and have a longer lifespan. LED PCBs contribute to this environmental friendliness by providing a durable and efficient base for the LEDs. In fact, by switching to LED lighting, the U.S. could save enough electricity to light 2.5 million homes for a year, according to the U.S. Department of Energy.
The Role of LED PCBs in the LED Lighting Industry
LED PCBs play a crucial role in the LED lighting industry. They provide the foundation for LED lights, enabling them to function efficiently and effectively. Here’s a closer look at their role:
1. Enabling High-Efficiency Lighting: LED PCBs, with their excellent heat dissipation capabilities, allow LEDs to operate at their maximum efficiency. This results in high-lumen output for each watt of power consumed, making LED lights one of the most energy-efficient lighting solutions available today.
2. Facilitating Compact Lighting Solutions: The compact size of LED PCBs allows for the creation of small, lightweight LED lighting solutions. This has enabled the development of innovative lighting products, such as LED strips and spotlights, that can fit into tight spaces and offer flexible installation options.
3. Supporting Long Lifespan: The effective heat management provided by LED PCBs contributes to the long lifespan of LED lights. By keeping the LEDs cool, LED PCBs help prevent premature LED failure and extend the life of the lighting product.
4. Driving Innovation: LED PCBs have been at the forefront of many innovations in the LED lighting industry. For example, the development of flexible LED PCBs has led to the creation of bendable LED lights that can be shaped to fit a variety of applications.
Applications of LED PCBs in Various Industries

LED PCBs are used in a wide range of industries due to their versatility, efficiency, and durability. Here are some key applications:
1. Residential and Commercial Lighting: LED PCBs are widely used in both residential and commercial lighting solutions, including downlights, spotlights, street lights, and architectural lighting. They offer energy-efficient, long-lasting, and aesthetically pleasing lighting solutions.
2. Automotive Industry: LED PCBs are used in various automotive applications, including headlights, interior lights, and indicator lights. They offer high brightness, low power consumption, and a long lifespan, making them ideal for automotive use.
3. Consumer Electronics: LED PCBs are used in a variety of consumer electronics, including TVs, computer monitors, and smartphones. They provide backlighting for LCD screens, offering high brightness and color accuracy.
4. Industrial Applications: In industrial settings, LED PCBs are used in machine vision systems, automation equipment, and safety lighting. They offer reliable, high-brightness lighting that can withstand harsh industrial conditions.
5. Medical Devices: LED PCBs are used in various medical devices, including surgical lighting and medical imaging systems. They offer high-intensity, adjustable lighting that can be tailored to specific medical applications.
In the next section, we’ll guide you on how to choose the right LED PCB for your needs. Stay tuned!
SMD LEDs in PCBs: A Detailed Look
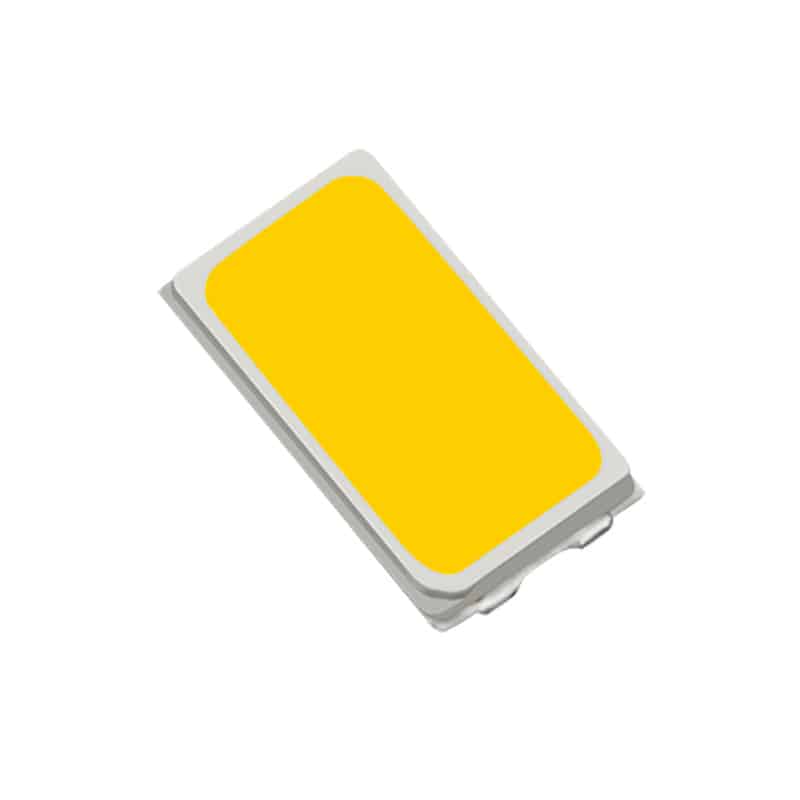

Surface-Mount Device (SMD) LEDs are a type of LED that are soldered onto the surface of a PCB. They are a popular choice for many applications due to their small size, high efficiency, and ease of assembly.
SMD LEDs come in a variety of sizes, with the most common being 2835, 3528, 5050, and 5730. The numbers refer to the dimensions of the LED chip. For instance, a 2835 SMD LED is 2.8mm by 3.5mm.
One of the main advantages of SMD LEDs is their compact size. This allows for a high density of LEDs on a PCB, which can result in a brighter light output. Additionally, SMD LEDs have excellent thermal performance, as the heat generated by the LED can be directly transferred to the PCB.
However, it’s important to note that the small size of SMD LEDs can also be a disadvantage. Due to their small size, they can be more difficult to handle and require precise placement on the PCB. This often requires specialized equipment and trained personnel.
Future Trends in LED PCB Technology
The LED PCB industry is constantly evolving, with new technologies and trends emerging regularly. Here are a few trends to watch out for:
- Mini and Micro LEDs: These are even smaller than SMD LEDs and offer higher brightness and efficiency. They are expected to be used in a variety of applications, including displays, automotive lighting, and wearable devices.
- Flexible LED PCBs: With the advent of flexible PCB materials, we can expect to see more flexible LED PCBs in the future. These can be bent and shaped to fit different applications, opening up new possibilities for LED lighting design.
- Smart LED PCBs: With the rise of the Internet of Things (IoT), we can expect to see more smart LED PCBs that can be controlled remotely and can adjust their light output based on external conditions.
- Increased energy efficiency: As energy efficiency becomes more important, we can expect to see continued improvements in the efficiency of LED PCBs.
Choosing the Right LED PCB for Your Needs
Choosing the right LED PCB for your needs is crucial to ensure the optimal performance and longevity of your LED lighting system. Here are some key factors to consider:
- LED Type: The type of LED used will significantly impact the performance of your PCB. SMD LEDs are popular due to their small size and high efficiency, but other types like COB or MCOB LEDs might be more suitable for certain applications due to their superior thermal management and light uniformity.
- PCB Material: The material of the PCB plays a crucial role in heat dissipation. Aluminum-based PCBs are commonly used in LED applications due to their excellent thermal conductivity, helping to prolong the lifespan of the LEDs.
- LED Density: The number of LEDs per unit area on the PCB, known as LED density, affects the brightness and heat generation. A higher LED density provides more brightness but also generates more heat, requiring better thermal management.
- Power Requirements: The power requirements of the PCB depend on the number and type of LEDs used. Ensure your power supply can handle the total power draw of all LEDs on the PCB.
- Size and Shape: The size and shape of the PCB should fit the physical constraints of your application. For instance, a compact device may require a small, round PCB, while a large lighting panel may need a large, rectangular one.
- Thermal Management: Effective thermal management is crucial to maintain the performance and extend the lifespan of LEDs. Consider PCBs with built-in heat sinks or those made from materials with high thermal conductivity.
- Cost: While it might be tempting to opt for the cheapest option, remember that the cost often reflects the quality. Investing in a high-quality LED PCB can save you money in the long run due to its better performance and longer lifespan.
- Customizability: Depending on your project, you might need a PCB that can be customized to your specific needs. Some manufacturers offer custom PCB design services to meet unique requirements.
Remember, the best LED PCB for your needs will depend on your specific application and requirements. It’s always a good idea to consult with a professional or do your own research before making a decision.
Get Access Now: www.rowsum.com
How to Design an LED PCB
Designing an LED PCB involves several steps, from conceptualizing the design to finalizing the layout. Here’s a basic guide:
1. Define Your Requirements: Start by defining the requirements of your LED PCB, such as the number of LEDs, the type of LEDs, the brightness level, and the power requirements.
2. Choose the Right Materials: Choose the right materials for your PCB. Aluminum is a popular choice for LED PCBs due to its excellent heat dissipation properties.
3. Design the Circuit: Design the circuit using a PCB design software. This involves placing the LEDs and other components on the PCB and routing the electrical connections between them.
4. Check the Design: Once the design is complete, check it for any errors or potential issues. This includes checking the circuit connections, the placement of components, and the thermal management.
5. Prototype and Test: Before moving to mass production, it’s a good idea to create a prototype of your LED PCB and test it. This allows you to identify and fix any issues before they become costly problems.
Designing an LED PCB can be a complex task, and it requires a good understanding of electronics and PCB design. If you’re not confident in designing your own LED PCB, consider working with a professional PCB manufacturer like Rowsum. They have the expertise and experience to design high-quality LED PCBs that meet your specific needs.
Manufacturing Process of LED PCBs
The manufacturing process of LED PCBs involves several steps:
1. PCB Fabrication: The PCB is fabricated based on the design. This involves etching the circuit pattern onto the PCB material, drilling holes for the components, and applying a solder mask.
2. LED Assembly: The LEDs and other components are then assembled onto the PCB. This is usually done using a process called Surface Mount Technology (SMT), where the components are soldered onto the surface of the PCB.
3. Testing: The assembled PCB is then tested to ensure it functions correctly. This includes electrical testing to check the circuit connections and thermal testing to ensure the PCB can effectively dissipate the heat generated by the LEDs.
4. Quality Control: The PCB undergoes quality control checks to ensure it meets the required standards. This includes visual inspection, functional testing, and reliability testing.
At Rowsum, we follow a rigorous manufacturing process to ensure the quality and reliability of our LED PCBs. We also offer custom PCB manufacturing services to meet your specific needs.
Quality Control and Testing of LED PCBs
Quality control and testing are crucial steps in the manufacturing process of LED PCBs. They ensure that the PCB functions correctly and meets the required standards.
1. Visual Inspection: The PCB is visually inspected for any obvious defects, such as misaligned components or soldering errors.
2. Electrical Testing: The PCB undergoes electrical testing to check the circuit connections. This involves applying a voltage to the PCB and measuring the resulting current.
3. Thermal Testing: The PCB is tested to ensure it can effectively dissipate the heat generated by the LEDs. This is crucial for the performance and longevity of the LEDs.
4. Reliability Testing: The PCB undergoes reliability testing to ensure it can withstand the conditions it will be exposed to in its intended application. This includes testing for resistance to heat, cold, vibration, and humidity.
At Rowsum, we take quality control and testing seriously. We follow a rigorous quality control process to ensure the reliability and performance of our LED PCBs.
Get Access Now: www.rowsum.com
Environmental Impact of LED PCBs
LED PCBs have a significant impact on the environment, much of it positive. Here’s a closer look at their environmental footprint:
1. Energy Efficiency: LED PCBs are highly energy-efficient, converting a high percentage of electrical energy into light with minimal waste heat. This efficiency reduces the demand on power plants and decreases greenhouse gas emissions.
2. Long Lifespan: LEDs have a longer lifespan compared to traditional lighting solutions, meaning fewer replacements and less waste. A longer lifespan also means fewer manufacturing resources are needed over time, further reducing their environmental impact.
3. No Hazardous Materials: Unlike fluorescent lights that contain mercury, LEDs do not contain any hazardous materials. This makes them safer to handle and reduces the environmental impact when they are disposed of.
4. Reduced Light Pollution: LED PCBs can be designed to direct light where it’s needed, reducing unnecessary light scatter. This precision can help reduce light pollution, which affects wildlife and obscures the night sky.
However, like all electronic products, LED PCBs do have some environmental impact. The manufacturing process requires energy and raw materials, and end-of-life disposal can contribute to electronic waste if not handled properly.
At Rowsum, we are committed to minimizing the environmental impact of our LED PCBs. We follow sustainable manufacturing practices and encourage responsible disposal and recycling of our products.
Conclusion
LED PCBs are a crucial component in the LED lighting industry, offering high efficiency, compact size, and a long lifespan. They come in various types and are used in a wide range of applications, from residential and commercial lighting to automotive and industrial applications.
While they have many advantages, it’s important to choose the right LED PCB for your specific needs. Factors to consider include the type of LED, the material of the PCB, the LED density, and the power requirements.
At Rowsum, we specialize in manufacturing high-quality LED PCBs. We offer custom PCB design services to meet your specific needs and follow a rigorous manufacturing process to ensure the quality and reliability of our products. If you’re looking for a reliable LED PCB manufacturer, consider Rowsum.
Get Access Now: www.rowsum.com
FAQs
1. What is an LED PCB?
An LED PCB is a Printed Circuit Board designed specifically for LED lighting. It provides a foundation for the LEDs and helps manage the heat they generate.
2. What are the advantages of LED PCBs?
LED PCBs offer several advantages, including high efficiency, compact size, long lifespan, and excellent thermal management.
3. What are the different types of LED PCBs?
There are several types of LED PCBs, including aluminum-based PCBs, copper-based PCBs, and flexible PCBs. The choice of PCB depends on the specific requirements of the LED lighting system.
4. How do I choose the right LED PCB for my needs?
Choosing the right LED PCB depends on several factors, including the type of LED, the size and shape of the PCB, the number of LEDs, and the power requirements. It’s always a good idea to consult with a professional or do your own research before making a decision.
5. What is the environmental impact of LED PCBs?
LED PCBs are generally environmentally friendly. They are energy-efficient, have a long lifespan, do not contain hazardous materials, and can help reduce light pollution. However, like all electronic products, they do have some environmental impact, particularly related to manufacturing and end-of-life disposal.